Exchange Rates in the Foreign Exchange Market
Introduction
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as the price of one currency in terms of another. This pivotal concept influences international trade, investment flows, and the overall economic health of nations. Understanding exchange rates is crucial for businesses, travelers, investors, and policymakers.
What is the Foreign Exchange Market?
The foreign exchange market, often referred to as Forex or FX, is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest and most liquid market in the world, with trillions of dollars traded daily. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as the value at which one currency can be exchanged for another.
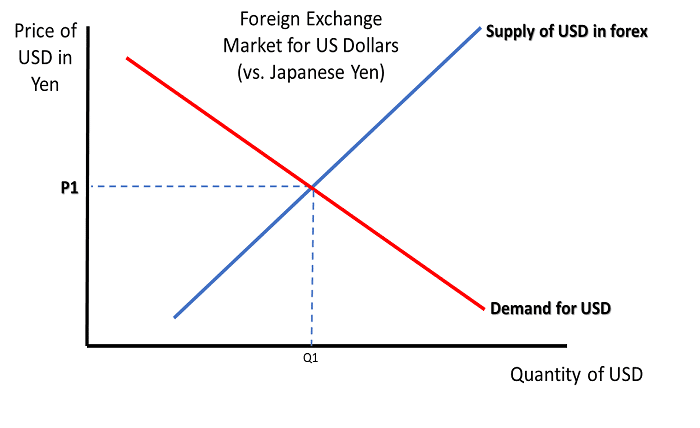
How Exchange Rates Are Determined
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by the interplay of supply and demand for currencies. Factors such as interest rates, inflation, political stability, and economic performance influence these dynamics. Central banks and monetary policies also play a crucial role in determining exchange rates.
Explore heartfelt and romantic Love Shayari, perfect for expressing your emotions. Find the best collection of Shayari to share with your loved ones.
Types of Exchange Rate Regimes
Countries adopt various exchange rate regimes to manage their currencies. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by these regimes, which can be broadly categorized into fixed, floating, and pegged exchange rate systems. Each regime has its own set of advantages and challenges.
Fixed Exchange Rate System
In a fixed exchange rate system, the exchange rate is defined and maintained at a set value against another currency or a basket of currencies. This system provides stability in international prices but requires significant foreign exchange reserves to maintain the fixed rate.
Floating Exchange Rate System
In a floating exchange rate system, the exchange rate is defined by market forces without direct government or central bank intervention. The value of the currency fluctuates based on supply and demand dynamics. This system allows for automatic adjustment of imbalances but can lead to increased volatility.
Discover VyvyManga a popular online platform for reading manga with a vast collection of titles, user-friendly features, and free access.
Pegged Exchange Rate System
A pegged exchange rate system is a hybrid where the exchange rate is defined relative to another currency but allows for some fluctuation within a specified range. This system combines the stability of fixed rates with the flexibility of floating rates.
The Impact of Exchange Rates on Global Trade
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as a critical factor influencing global trade. Exchange rates affect the competitiveness of exports and imports, pricing strategies, and profit margins for international businesses. Fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact a country’s trade balance.
Exchange Rates and Investment Decisions
Investors closely monitor exchange rates as they influence the return on international investments. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as a key determinant of investment flows, affecting decisions related to foreign direct investment (FDI), portfolio investments, and currency speculation.
Hedging Against Exchange Rate Risk
Businesses and investors often use hedging strategies to protect against adverse exchange rate movements. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as a source of risk that can be managed through forward contracts, options, and other financial instruments designed to mitigate potential losses.
The Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a vital role in the foreign exchange market. They can influence exchange rates through monetary policy decisions, foreign exchange interventions, and managing currency reserves. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined and sometimes manipulated by central banks to achieve economic objectives.
Conclusion
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as a cornerstone of international finance, impacting trade, investment, and economic stability. Understanding how exchange rates are determined and managed helps individuals and businesses navigate the complexities of global markets. Whether you’re a traveler, investor, or policymaker, staying informed about exchange rate dynamics is essential for making sound financial decisions.
FAQs
1. What factors influence exchange rates in the foreign exchange market?
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by factors such as interest rates, inflation, political stability, economic performance, and central bank policies.
2. How does a fixed exchange rate system work?
In a fixed exchange rate system, the exchange rate is defined and maintained at a set value against another currency or a basket of currencies, providing stability but requiring substantial foreign exchange reserves.
3. What is the difference between floating and pegged exchange rate systems?
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as floating when it fluctuates based on market forces, while a pegged exchange rate allows for some controlled fluctuation around a fixed value.
4. Why are exchange rates important for international trade?
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as a key factor that affects the competitiveness of exports and imports, influencing pricing strategies and profit margins for international businesses.
5. How can businesses hedge against exchange rate risk?
Businesses can use hedging strategies such as forward contracts, options, and other financial instruments to manage the risk associated with exchange rate fluctuations in the foreign exchange market.