Foreign Exchange Market: The Definition and Impact of Exchange Rates
Introduction
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as the price of one currency in terms of another. This crucial financial metric influences global trade, investment, and economic stability. Understanding exchange rates, their determinants, and their impact is essential for businesses, investors, and policymakers.
What is the Foreign Exchange Market?
The foreign exchange market, or forex market, is a global decentralized platform where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as the value at which one currency can be exchanged for another, making it a cornerstone of international financial transactions.
How Exchange Rates Are Determined
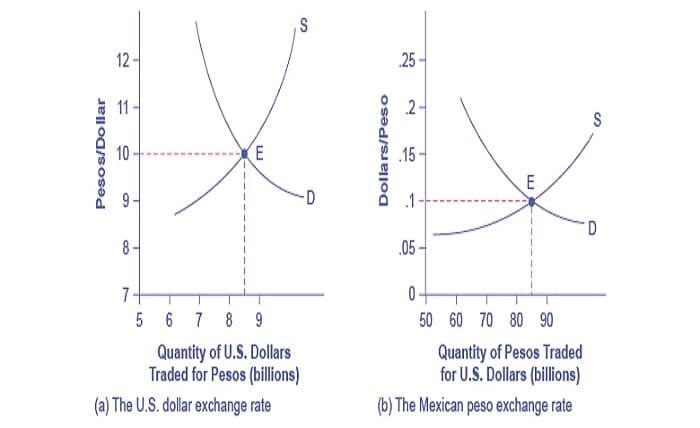
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by various factors, including supply and demand dynamics, economic indicators, and geopolitical events. Market participants, such as banks, corporations, and individual traders, influence these rates through their trading activities. Understanding how these factors interplay can provide insights into the movement of exchange rates.
Types of Exchange Rates
There are several types of exchange rates in the foreign exchange market. The exchange rate is defined differently in various contexts, such as fixed, floating, and pegged rates. Fixed rates are set by governments, floating rates fluctuate based on market forces, and pegged rates are tied to another currency or a basket of currencies. Each type has its own implications for economic policy and stability.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by multiple factors. Key influences include interest rates, inflation rates, political stability, and economic performance. For example, higher interest rates typically attract foreign capital, leading to an appreciation of the currency. Understanding these factors helps in predicting and analyzing exchange rate movements.
Impact of Exchange Rates on Global Trade
Exchange rates play a crucial role in global trade. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as a key determinant of the cost of exporting and importing goods and services. A favorable exchange rate can boost a country’s exports by making its goods cheaper for foreign buyers, while an unfavorable rate can have the opposite effect.
Strategies for Trading in the Forex Market
Effective trading strategies are essential for success in the forex market. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as a crucial element for traders who employ techniques such as technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and leverage. These strategies help traders make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
The Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a significant role in the foreign exchange market. The exchange rate is defined as a tool for implementing monetary policy. Central banks can influence exchange rates through interventions, such as buying or selling currencies, and by setting interest rates. Their actions can stabilize or destabilize currency values, impacting the broader economy.
Exchange Rate Mechanisms and Policies
Different countries adopt various exchange rate mechanisms and policies. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by these mechanisms, which can include managed float systems, currency boards, and monetary unions. Understanding these policies provides insights into how countries maintain economic stability and competitiveness.
Historical Perspectives on Exchange Rates
Historical analysis of exchange rates offers valuable lessons for the present. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by historical events, such as the Bretton Woods Agreement and the shift to floating exchange rates in the 1970s. These historical shifts have shaped the current structure and functioning of the forex market.
Future Trends in the Foreign Exchange Market
The future of the foreign exchange market is likely to be influenced by technological advancements and global economic trends. In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by emerging factors such as digital currencies, fintech innovations, and changes in international trade policies. Keeping abreast of these trends is crucial for staying competitive in the forex market.
Conclusion
In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined as a critical economic indicator that impacts global trade, investment, and economic policy. Understanding the factors that influence exchange rates, the role of central banks, and effective trading strategies can help businesses, investors, and policymakers navigate this complex market. By staying informed about historical and future trends, stakeholders can make more informed decisions and contribute to economic stability.
FAQs
- What is the foreign exchange market? The foreign exchange market, or forex market, is a global decentralized platform where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market, influencing global trade and investment.
- How are exchange rates determined? In the foreign exchange market, the exchange rate is defined by factors such as supply and demand, economic indicators, and geopolitical events. Market participants influence these rates through trading activities.
- What types of exchange rates exist? Exchange rates in the foreign exchange market include fixed, floating, and pegged rates. Each type has different implications for economic policy and stability.
- What role do central banks play in exchange rates? Central banks influence exchange rates through interventions and monetary policy, such as buying or selling currencies and setting interest rates, impacting the broader economy.
- What are some effective trading strategies in the forex market? Effective trading strategies include technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and leverage. These strategies help traders make informed decisions and manage risks in the foreign exchange market.





